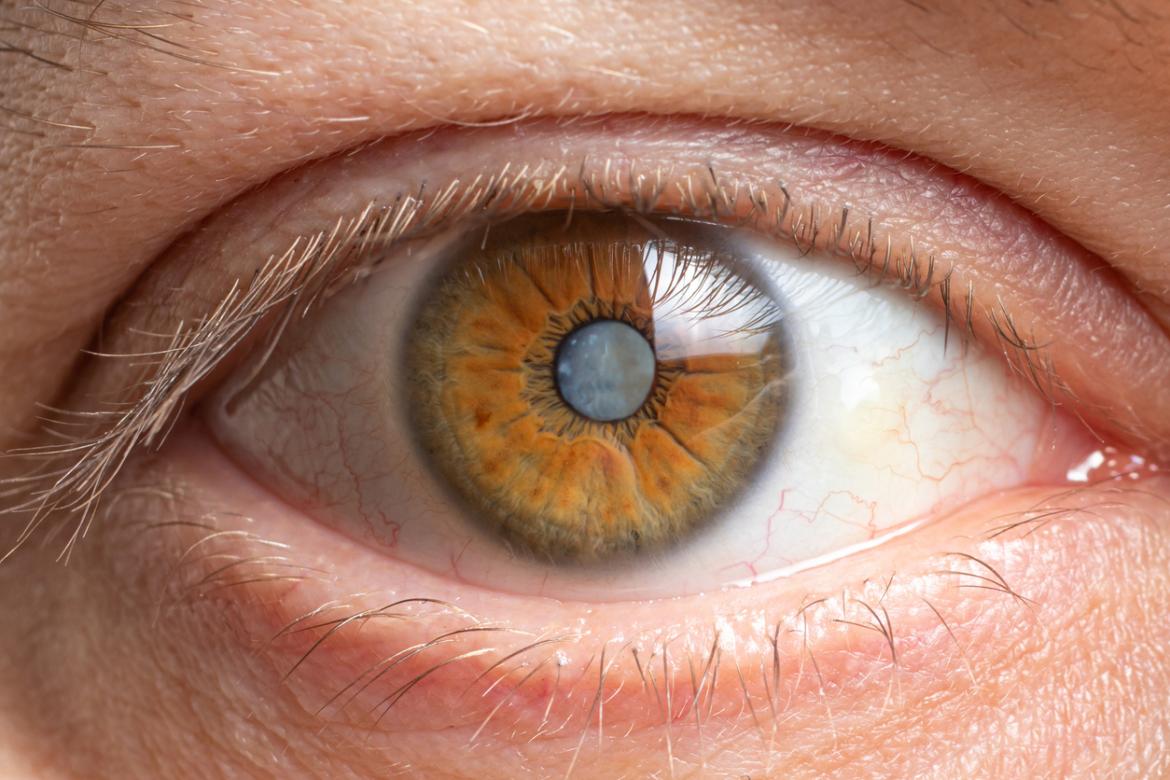
Cataracts are a common condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the signs that indicate you may need cataract eye surgery can empower you to seek treatment in a timely manner. This article will explore the nature of cataracts, their symptoms, risk factors, and guidelines for considering surgery.
Understanding Cataracts: A Brief Overview
Cataracts develop when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy, impairing vision. This condition is often associated with aging but can affect individuals of all ages due to various factors. A comprehensive understanding of cataracts is essential for recognizing when surgical intervention may be necessary.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of cataracts, understanding their implications, and evaluating one’s situation regarding cataract eye surgery are essential components of eye health. Regular consultations with eye care professionals can facilitate early detection and treatment, ultimately guiding you towards a healthier vision.
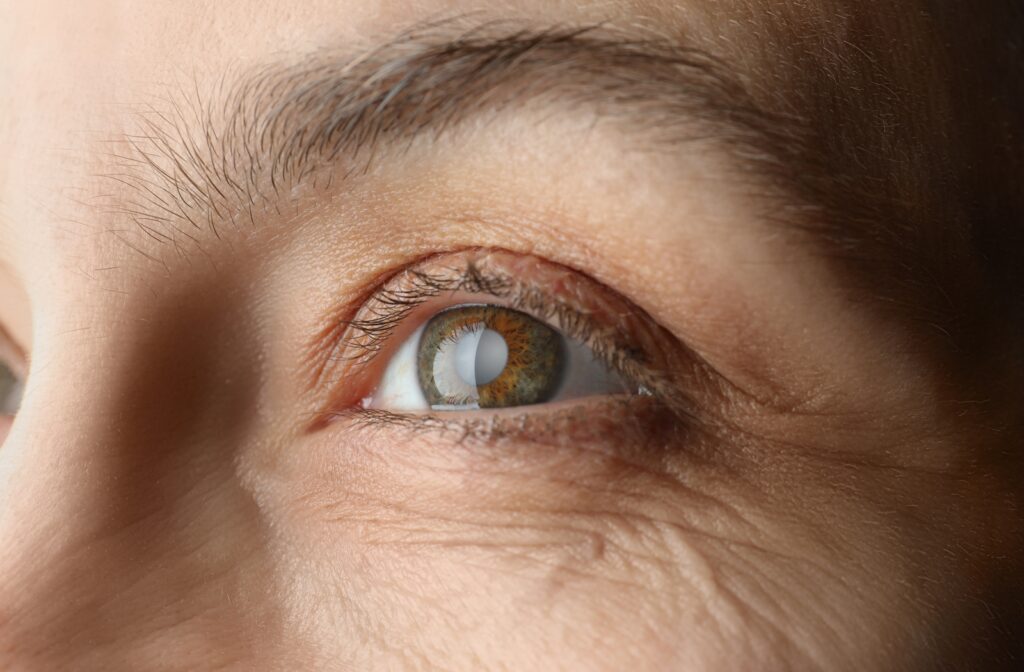
What are Cataracts?
Cataracts are characterized by the gradual opacification of the eye’s lens, which ultimately obstructs the passage of light to the retina. This clouding can lead to blurred vision, double vision, and even a complete loss of sight if left untreated.
The progression of cataracts can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience slow, subtle changes in their vision, while others may notice more rapid deterioration. Understanding the nature of cataracts is crucial for recognizing when to take action. In many cases, patients report that their vision becomes increasingly hazy, and they may find it difficult to read, drive, or perform everyday tasks. This gradual decline can significantly impact quality of life, making it essential for individuals to be aware of the signs and symptoms associated with cataracts.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cataracts
The development of cataracts is primarily influenced by age, but several other risk factors can contribute to their formation. These include prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light, tobacco use, diabetes, and prolonged use of corticosteroid medications. Additionally, a family history of cataracts can increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Understanding these risk factors can help in taking proactive steps toward eye health, such as regular eye examinations and protective measures against UV light exposure. For instance, wearing sunglasses that block UV rays can be a simple yet effective way to reduce the risk of cataracts. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, may also play a role in protecting the eyes from oxidative stress that can lead to cataract formation. Engaging in regular physical activity and managing chronic conditions like diabetes can further enhance overall eye health and potentially delay the onset of cataracts. Read more about diabetes on https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes
Common Symptoms Indicating Cataract
Recognizing the symptoms of cataracts is key to understanding when surgery may be necessary. Early detection can lead to timely intervention and improved quality of life.
Changes in Vision
One of the first signs of cataracts is a gradual change in vision. Individuals may experience blurriness, dimness, or a noticeable decrease in visual acuity. These changes can make daily activities, such as reading or driving, increasingly challenging.
Furthermore, the perception of colors may fade, leaving objects appearing dull and less vibrant. Regularly monitoring these visual changes can provide valuable insight into whether surgery is required. In some cases, individuals may also notice that their vision fluctuates, with periods of clarity followed by episodes of blurriness. This inconsistency can be frustrating and may lead to increased reliance on glasses or contact lenses, which may no longer provide the same level of correction as before.
Sensitivity to Light
Many individuals with cataracts report increased sensitivity to light. This symptom can manifest as difficulty seeing in bright sunlight or artificial light, leading to discomfort and a sense of glare.
Such sensitivity may also cause visual impairment in low-light conditions or contrast-rich settings. This symptom often prompts individuals to seek medical advice and could indicate that cataract surgery is warranted. Additionally, some people may find themselves squinting more often or needing to wear sunglasses even on overcast days, as their eyes struggle to adapt to varying light conditions. This heightened sensitivity can significantly affect outdoor activities and social interactions, leading to a more isolated lifestyle. Click here to find more about interactions.
Difficulty with Night Vision
As cataracts progress, many individuals find that their night vision deteriorates significantly. This change may result in halos around lights, making driving at night particularly hazardous.
Difficulty seeing in the dark can impact one’s ability to navigate safely, further emphasizing the need for timely evaluation by an eye care professional. In addition to halos, some individuals may experience a significant reduction in depth perception, making it challenging to judge distances accurately. This can be especially concerning for those who enjoy nighttime activities or have jobs that require working in dimly lit environments. The cumulative effect of these symptoms can lead to increased anxiety and reluctance to engage in evening outings, further highlighting the importance of addressing cataract symptoms promptly.
The Link Between Age and Cataracts
Aging is the primary factor associated with the development of cataracts. Understanding how age correlates with cataracts can provide insight into when individuals should start monitoring their eye health more closely.
Cataracts in the Elderly
The prevalence of cataracts increases significantly among older adults. By the age of 80, more than half of all Americans have cataracts or have undergone surgery to remove them. This condition, characterized by the clouding of the lens in the eye, can lead to blurred vision, increased glare from lights, and difficulty seeing at night. Such visual impairments can significantly affect the quality of life, making it essential for older adults to remain vigilant about their eye health.
Regular eye examinations become increasingly crucial as individuals age, ensuring that any necessary interventions, including surgery, are implemented in a timely manner. Eye care professionals often recommend that seniors schedule comprehensive eye exams at least once a year. During these visits, eye doctors can assess not only the presence of cataracts but also other age-related eye conditions such as glaucoma and macular degeneration, which can further complicate vision health.
Early Onset Cataracts
While cataracts in the elderly are common, early-onset cataracts can occur due to genetic factors, certain diseases, or lifestyle choices. Individuals experiencing symptoms at a younger age should seek prompt medical advice. Factors such as prolonged exposure to UV light, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of developing cataracts earlier in life. Additionally, conditions like diabetes can accelerate the formation of cataracts, making it vital for those with such health issues to monitor their eye health closely.
Early detection and treatment can help prevent more serious complications from developing, highlighting the importance of awareness and regular check-ups. For younger individuals diagnosed with cataracts, treatment options may include lifestyle modifications, such as improved nutrition and UV protection, alongside potential surgical interventions. Engaging in a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and regular exercise, can also contribute to overall eye health and potentially delay the onset of cataracts, emphasizing the role of prevention in eye care.
Diagnosis of Cataracts
Diagnosing cataracts involves a comprehensive eye examination by a licensed ophthalmologist. Various tests can help determine the presence and severity of cataracts, guiding the decision-making process regarding surgery.
Eye Examination Procedures
During an eye exam, the eye care professional will conduct multiple tests, including visual acuity assessments and slit-lamp examinations. These tests allow for a thorough evaluation of the lens and overall eye health. The visual acuity test measures how well you can see at various distances, often using an eye chart. The slit-lamp examination provides a magnified view of the eye’s structures, enabling the ophthalmologist to observe any cloudiness in the lens that may indicate cataracts.
In some cases, advanced imaging technology may be utilized to obtain a more detailed view of the lens, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) can provide cross-sectional images of the retina and other eye structures, helping to identify any additional issues that may accompany cataracts, such as macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy.
Interpreting Your Eye Test Results
After the examinations are complete, the eye care professional will discuss the results with you. This discussion will encompass the severity of the cataracts, potential treatment options, and whether surgery would be recommended based on your specific circumstances. The severity of cataracts is often categorized into stages, ranging from mild to advanced, which can influence the urgency of treatment. For example, mild cataracts may only require regular monitoring, while advanced cases could necessitate surgical intervention to restore vision.
Understanding your eye test results is crucial for making informed decisions about your eye health and the potential need for surgical intervention. The ophthalmologist will also explain the implications of your results on your daily life, such as how cataracts can affect activities like reading, driving, or watching television. Additionally, they may discuss lifestyle changes or assistive devices that could help manage symptoms while you consider your treatment options. This collaborative approach ensures that you feel empowered and informed as you navigate your eye care journey.
When to Consider Cataract Surgery
Deciding to undergo cataract surgery is an important choice that requires careful consideration. There are specific indicators and personal factors that can help guide this decision.

Assessing Your Quality of Life
Individuals should reflect on how cataracts are impacting their daily activities and overall quality of life. If vision loss has begun to interfere with work, hobbies, or essential tasks, surgery may be a viable option.
Assessing your ability to perform everyday tasks can provide valuable insight into whether the benefits of cataract surgery outweigh the risks, guiding your decision.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
Before deciding on surgery, it is essential to have a thorough discussion with your eye care professional regarding the benefits and potential risks associated with the procedure. Most cataract surgeries are safe and effective, but understanding the risks allows individuals to make an informed choice.
Weighing the risks against the potential improvement in vision and quality of life is a critical step in determining the appropriateness of cataract surgery.
Other resources: A Step-by-Step Guide to Cataract Surgery Sydney